Valid Binary Search Tree (20250730)
- Question
-
Given the root of a binary tree, return true if it is a valid binary search tree, otherwise return false.
- A valid binary search tree satisfies the following constraints:
- The left subtree of every node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
- The right subtree of every node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
- Both the left and right subtrees are also binary search trees.
- Example 1:
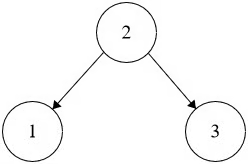
Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: true
- Example 2:
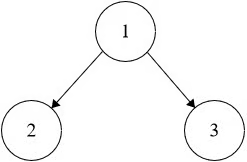
Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: false
-
- Solution 1:
- Threads: Traverse whole tree, if left or right child do not fulfill the constrants, return False.
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right from collections import deque class Solution: def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool: q = collections.deque() q.append(root) # while q not None: while q: node = q.popleft() if not (node.val > node.left.val and node.val < node.right.val): return False # if node.left not None: if node.left is not None: q.append(node.left) # if node.right not None: if node.right is not None: q.append(node.right) return Trueif not (node.val > node.left.val and node.val < node.right.val): ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'val' -
Issue:
if not (node.val > node.left.val and node.val < node.right.val)- This will crash if node.left or node.right is None. - Second try:
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right from collections import deque class Solution: def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool: q = collections.deque() q.append(root) # while q not None: while q: node = q.popleft() node_left = node.left node_right = node.right if node_left is not None and node.val <= node_left.val: return False if node_right is not None and node.val >= node_right.val: return False # if node.left not None: if node.left is not None: q.append(node.left) # if node.right not None: if node.right is not None: q.append(node.right) return TrueWrong Answer Input: root=[5,4,6,null,null,3,7] Your Output: true Expected output: false - Third try:
- Recursive check from buttom to top.
- Find: 1. left tree biggest. 2. Right tree smallest.
- 1 < node.val < 2 ```python # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def init(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right
class Solution: def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool: def dfs(node, low, high): if not node: return True if not (low < node.val < high): return False return dfs(node.left, low, node.val) and dfs(node.right, node.val, high)
return dfs(root, float('-inf'), float('inf')) ``` > This version's code is assisted by ChatGPT. - ✅ **往左走,更新上界;往右走,更新下界**-
🔁 遞迴邏輯快速回顧
return dfs(node.left, low, node.val) and dfs(node.right, node.val, high)- 左子樹只能在
low ~ node.val間 - 右子樹只能在
node.val ~ high間 - 這個界線會一直往下傳,讓每個節點都受到所有祖先節點的限制。
- 左子樹只能在
- Solution 4: Breath First Search
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool: if not root: return True q = deque([root, float('-inf'), float('inf')]) while q: node, left, right = q.popleft() if not (left < node.val < right): return False if node.left: q.append((node.left, left, node.val)) if node.right: q.append((node.right, node.val, right)) return True
Hint 1: A brute force solution would involve traversing the tree and, for every node, checking its entire left subtree to ensure all nodes are less than the current node, and its entire right subtree to ensure all nodes are greater. This results in an O(n^2) solution. Can you think of a better way? Maybe tracking values during the traversal would help.
Hint 2: We can use the Depth First Search (DFS) algorithm to traverse the tree. At each node, we need to ensure that the tree rooted at that node is a valid Binary Search Tree (BST). One way to do this is by tracking an interval that defines the lower and upper limits for the node’s value in that subtree. This interval will be updated as we move down the tree, ensuring each node adheres to the BST property.
Hint 3: We start with the interval [-infinity, infinity] for the root node. As we traverse the tree, when checking the left subtree, we update the maximum value limit because all values in the left subtree must be less than the current node’s value. Conversely, when checking the right subtree, we update the minimum value limit because all values in the right subtree must be greater than the current node’s value.
-
Note: BFS v.s. DFS
演算法 Recursive Iterative (Stack/Queue) 常見寫法 DFS ✅ ✅(用 stack) 兩種都常見 BFS ❌ ✅(用 queue) 幾乎只用 iterative
- Threads: Traverse whole tree, if left or right child do not fulfill the constrants, return False.